Here are some science questions to help you test your general science knowledge. They will also show you which of the Florida, Utah, and NGSS science standards each question is testing.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
Get 5 more random questions.
Would you rather see the most recently added questions?
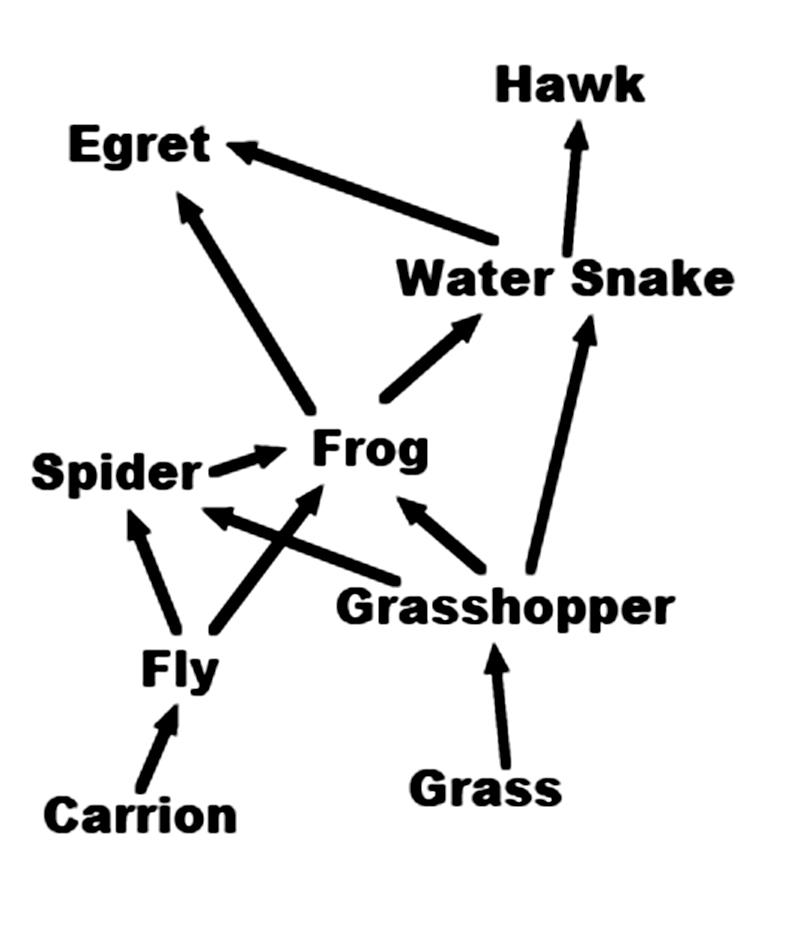
This is a simple chart showing how energy flows through some of the parts of a food web. For example, the arrow from the grass to the grasshopper shows that the grasshopper gets it energy by eating the grass.
The hawk gets its energy by eating the water snake, but there is no arrow leading from the hawk. What should the arrow from the hawk point to>
-
Egret
No. The egret does not eat hawks. -
Carrion
Yes! Carrion is dead animals. When the hawk eventually dies, flies will get their energy by eating the dead body. You could also draw arrows from all of the other animals to carrion. -
The Sun
No. The Sun is not on the chart, and The Sun does not get its energy from the hawk. -
There should not be an arrow leading from the hawk.
No. Energy cannot be destroyed. It always goes back into the system.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.L.17.3 Trace the flow of energy from the Sun as it is transferred along the food chain through the producers to the consumers.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
SC.8.L.18.4 Cite evidence that living systems follow the Laws of Conservation of Mass and Energy.
| Thoughts on Trees | text page |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS3-1 Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
5-LS2-1 Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |

When a scientist makes a new discovery, other scientists usually do exactly the same experiment. Why?
-
They want to get part of the credit.
No. While replicating an experiment is very important, the scientists who do it usually don't get much credit for their work unless they discover an error in the original experiment. -
Repetition is part of the scientific process.
No. Repetition is when scientists repeat their own experiment several times, not when other scientists do the same experiment. -
They think they can make changes to improve the experiment.
No. By doing exactly the same experiment, they are not changing anything. Instead, they are replicating the experiment as closely as possible. -
Replication is part of the scientific process.
Yes. By replicating the experiment, other scientists can help verify that the results are accurate. There is always a possibility that there was some unnoticed influence on the original experiment, and replication can help spot that.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.2.N.1.4 Explain how particular scientific investigations should yield similar conclusions when repeated.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
SC.5.N.2.2 Recognize and explain that when scientific investigations are carried out, the evidence produced by those investigations should be replicable by others.
>>> Teacher Page: Nature of Science and Dissolving
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
SC.6.N.1.2 Explain why scientific investigations should be replicable.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
SC.7.N.1.2 Differentiate replication (by others) from repetition (multiple trials).
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
SC.8.N.1.2 Design and conduct a study using repeated trials and replication.
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
Utah
NGSS

Which of these is NOT a form of energy?
-
Light
No. Light is a form of kinetic energy. -
Thermal
No. Thermal is a form of kinetic energy. -
Fire
Yes. Fire is a chemical reaction that can produce forms of energy such as light, heat, and motion, but fire is NOT a form of energy. -
Motion
No. Motion is a form of kinetic energy.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.3 Recognize that humans need resources found on Earth and that these are either renewable or nonrenewable.
| Recycle | video |
| Review Energy-4 | quest |
| Review Energy-1 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
4-ESS3-1 Obtain and combine information to describe that energy and fuels are derived from natural resources and their uses affect the environment.
| Investigating Acid Rain | video, checked |
| Solar Power | video, checked |
| Review Energy-4 | quest |
| Review Energy-1 | practice |
5-ESS3-1 Obtain and combine information about ways individual communities use science ideas to protect the Earth’s resources and environment.
| Recycle | video |
| Review Energy-4 | quest |

Which of the following observations is scientifically testable?
-
Honeybees are good insects.
No. "Good" is a generic term that could mean many different things in different situations. It is an opinion, not a testable property. This statement is NOT scientifically testable. -
Honeybees are important insects.
No. "Important" is a generic term that could mean many different things to different people. It is an opinion, not a testable property. This statement is NOT scientifically testable. -
Honeybees are pretty insects.
No. Some people might think that a honeybee is pretty, and some people might not. It is an opinion, not a testable property. This statement is NOT scientifically testable. -
Honeybees are not insects.
Yes! While this statement is not correct, it is scientifically testable. You could examine the bee to see that it does fit the definition of an insect. This statement is IS scientifically testable.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.N.2.1 Recognize and explain that science is grounded in empirical observations that are testable; explanation must always be linked with evidence.
| My Position on Science and Religion | video |
| What is Science?: Objective | video |
| Mobius Strip | video |
| Is Your Project Scientifically Testable? | text page |
| Is Your Project Scientifically Testable? Part 2 | text page |
| Review Scientific Process-3 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-4 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-8 | practice |
SC.8.N.2.1 Distinguish between scientific and pseudoscientific ideas.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Feeding Bread to Birds | text page |
| Fact checking GMOs | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part four | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part three | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part two | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part one | text page |
| Review Scientific Process-3 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-4 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-8 | practice |
Utah
NGSS

Which part of the food web do these termites belong to?
-
Producer.
No. A producer captures energy from sunlight, and stores it as food. To do that, the organism needs to contain chlorophyll. -
Primary Consumer.
No. Primary consumers eat producers. Termites do not eat live plants. -
Secondary Consumer
No. Secondary consumers eat other consumers. This butterfly does not eat animals. -
Decomposer
Yes! Termites are one of the few animals that can digest the cellulose from dead wood, thanks to special bacteria that live inside them. That makes termites very important as decomposers, but it also means that they can be a problem when we build things from wood.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.L.17.3 Trace the flow of energy from the Sun as it is transferred along the food chain through the producers to the consumers.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
SC.7.L.17.1 Explain and illustrate the roles of and relationships among producers, consumers, and decomposers in the process of energy transfer in a food web.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS3-1 Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
5-LS2-1 Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
