Here are some science questions to help you test your general science knowledge. They will also show you which of the Florida, Utah, and NGSS science standards each question is testing.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
Get 5 more random questions.
Would you rather see the most recently added questions?
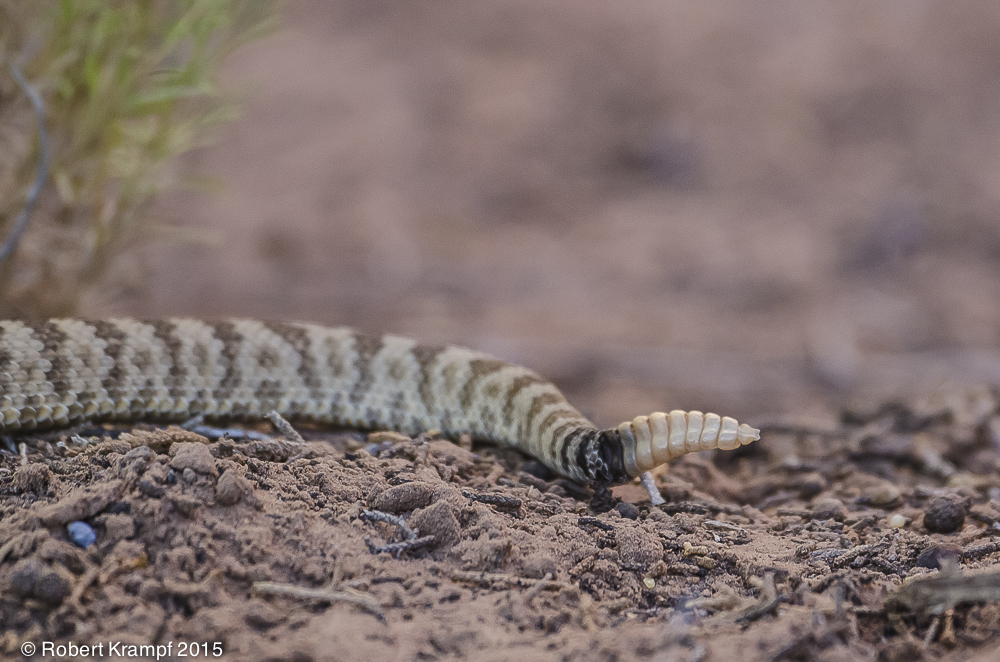

The rattle on a Rattlesnake is an adaptation that:
-
attracts a mate.
No. Snakes do not hear airborne sounds, so another snake would not hear the rattle. -
attracts mice and other prey animals.
No. Like other animals, mice would be frightened away by the rattle. -
warns predators to stay away.
Yes! The sound of a Rattlesnake's rattle is a warning that the snake will bite to defend itself. -
helps the snake hide.
No. There is nothing about the rattle that would serve as camouflage or help the snake hide.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.L.17.1 Compare and contrast adaptations displayed by animals and plants that enable them to survive in different environments such as life cycles variations, animal behaviors and physical characteristics.
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Nature Watching | video, checked |
| Calling a Woodpecker | video, checked |
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Seed Search | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Flowers | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| Review Plants-1 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-2 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-3 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-4 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.V.4.d Compare the structure and behavior of Utah amphibians and reptiles.
| A Walk in the Park | video, checked |
| Nature Watching | video, checked |
| Review Adaptation-2 | practice |
UT.7.IV.2.a Predict why certain traits (e.g., structure of teeth, body structure, coloration) are more likely to offer an advantage for survival of an organism.
| Selective Smelling | video, checked |
| Onion Crystals | video |
| Who Evolved on First? | text page, free, checked |
| Thoughts on an Exoskeleton | text page, free |
| Review Adaptation-1 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-2 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-5 | practice |
| Review Adaptation-6 | practice |
NGSS

Baking a cake is an example of:
-
A physical change
Partly right. Some of the changes involved in baking a cake are physical changes. -
A chemical change
Partly right. Some of the changes involved in baking a cake are chemical changes. -
Both
Yes! The process of baking a cake involves many changes. Some, such as water evaporating and sugar melting are physical changes. Others, such as baking powder reacting cause a change in the chemical formulas, indicating a chemical change. For more on this, read Changing How We Look at Changing -
Neither
No. There are many changes involved in baking a cake.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.P.9.1 Investigate and describe that many physical and chemical changes are affected by temperature.
| The Chemistry of Milk | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Why Wet Things Don't Burn | video, checked |
| Igneous Sugar | video, checked |
| Changing How We Look at Changing | text page, free |
| Growing Crystals from Solution | text page, checked |
| Review Matter-4 | practice |
SC.8.P.9.2 Differentiate between physical changes and chemical changes.
| Changing Colors, part 1 | video |
| Changing Colors, part 2 | video |
| Making Butter | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Polymers and Slime | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Silver Pictures | video, checked |
| Chemical and Physical Changes | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Changing How We Look at Changing | text page, free |
| Review Matter-4 | practice |
Utah
UT.5.I.3.d Compare a physical change to a chemical change.
| Changing Colors, part 1 | video |
| Changing Colors, part 2 | video |
| The Chemistry of Milk | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Making Butter | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Chemical and Physical Changes | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Paper Petals | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Changing How We Look at Changing | text page, free |
| Review Matter-4 | practice |
UT.8.I.1.a Differentiate between chemical and physical properties.
| Cabbage Indicator | video, checked |
| Making Butter | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Making Turmeric Paper | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Chemical and Physical Changes | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Paper Petals | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Matter-4 | practice |
NGSS
2-PS1-4 Construct an argument with evidence that some changes caused by heating or cooling can be reversed and some cannot.
| The Chemistry of Milk | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| A Watched Pot | video |
| Why We Sweat | video, checked |
| Photographing Snowflakes | video, checked |
| Ice Cream Science | video, checked |
| A Hot Change | text page |
| Review Matter-4 | practice |
MS-PS1-2 Analyze and interpret data on the properties of substances before and after the substances interact to determine if a chemical reaction has occurred.
| Making Turmeric Paper | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Relighting Candles | video, checked |
| Catalysts | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Changing Colors, part 1 | video |
| Chemical and Physical Changes | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Changing Colors, part 2 | video |
| The Chemistry of Milk | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| How They Get the Sparks in a Sparkler | video |
| Orange Flash | video |
| Candles in a Jar, part 2 | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Candles in a Jar, part 1 | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Cabbage Indicator | video, checked |
| Polymers and Slime | video, free, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Silver Pictures | video, checked |
| Science and the Haunted Pumpkin | video, free, checked |
| A Hot Change | text page |
| Changing How We Look at Changing | text page, free |
| Review Matter-4 | practice |
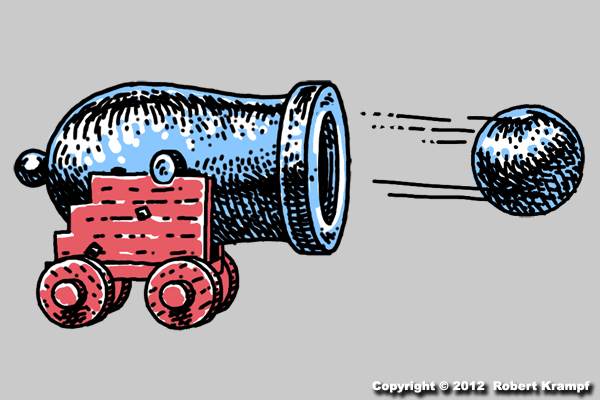
When this cannon fires, cannon and the cannon ball both move, but the cannon ball moves much farther and faster than the cannon. Why?
-
The cannon ball is smaller.
No. While smaller size means a little less air resistance, that is not enough to cause the difference. -
The wheels on the cannon are stuck.
No. Even with the wheels moving freely, the cannon ball will still move much faster and much farther. -
The cannon ball is round.
No. While the round shape means a little less air resistance, that is not enough to cause the difference. -
The cannon ball weighs less.
Yes! According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, the more mass an object has, the less it will be affected by a force. Newton's Third Law of Motion tells us that the cannon and the cannon ball will both be pushed by the same amount of force, but since the cannon is much heavier (more mass), it will not move as fast or as far.If the cannon was made of very light weight plastic, so that it was much ligher (less mass) than the cannon ball, then the cannon would move farther and faster.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.P.13.3 Investigate and describe that the more mass an object has, the less effect a given force will have on the object's motion.
| The Difference Between Weight and Mass | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Wrong Way Balloon | video, checked |
| High Bounce | video, checked |
| Review Force and Motion-1 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-2 | practice |
Utah
UT.3.III.2.b Compare and chart the relative effects of a force of the same strength on objects of different weight (e.g., the breeze from a fan will move a piece of paper but may not move a piece of cardboard).
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| High Bounce | video, checked |
| Review Force and Motion-1 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-2 | practice |
NGSS
MS-PS2-2 Plan an investigation to provide evidence that the change in an object’s motion depends on the sum of the forces on the object and the mass of the object.
| Raw Egg or Boiled? | video, checked |
| More Science of Balance | video, checked |
| Science of Balance | video, checked |
| The Old Tablecloth Trick | video |
| Bernoulli Effect | video |
| Smoke Rings | video |
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| The Difference Between Weight and Mass | video, checked |
| Torque | video |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Newton's First Law of Motion | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| Wrong Way Balloon | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 2 | video, checked |
| Strange Flame, part 1 | video, checked |
| Science Friction | video, checked |
| Balancing a Meter Stick | text page |
| Review Force and Motion-1 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-2 | practice |
| Review Force and Motion-4 | practice |

Which of the following observations is scientifically testable?
-
Honeybees are good insects.
No. "Good" is a generic term that could mean many different things in different situations. It is an opinion, not a testable property. This statement is NOT scientifically testable. -
Honeybees are important insects.
No. "Important" is a generic term that could mean many different things to different people. It is an opinion, not a testable property. This statement is NOT scientifically testable. -
Honeybees are pretty insects.
No. Some people might think that a honeybee is pretty, and some people might not. It is an opinion, not a testable property. This statement is NOT scientifically testable. -
Honeybees are not insects.
Yes! While this statement is not correct, it is scientifically testable. You could examine the bee to see that it does fit the definition of an insect. This statement is IS scientifically testable.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.N.2.1 Recognize and explain that science is grounded in empirical observations that are testable; explanation must always be linked with evidence.
| My Position on Science and Religion | video |
| What is Science?: Objective | video |
| Mobius Strip | video |
| Is Your Project Scientifically Testable? | text page |
| Is Your Project Scientifically Testable? Part 2 | text page |
| Review Scientific Process-3 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-4 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-8 | practice |
SC.8.N.2.1 Distinguish between scientific and pseudoscientific ideas.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Feeding Bread to Birds | text page |
| Fact checking GMOs | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part four | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part three | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part two | text page |
| I Saw It on the Internet, part one | text page |
| Review Scientific Process-3 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-4 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-8 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
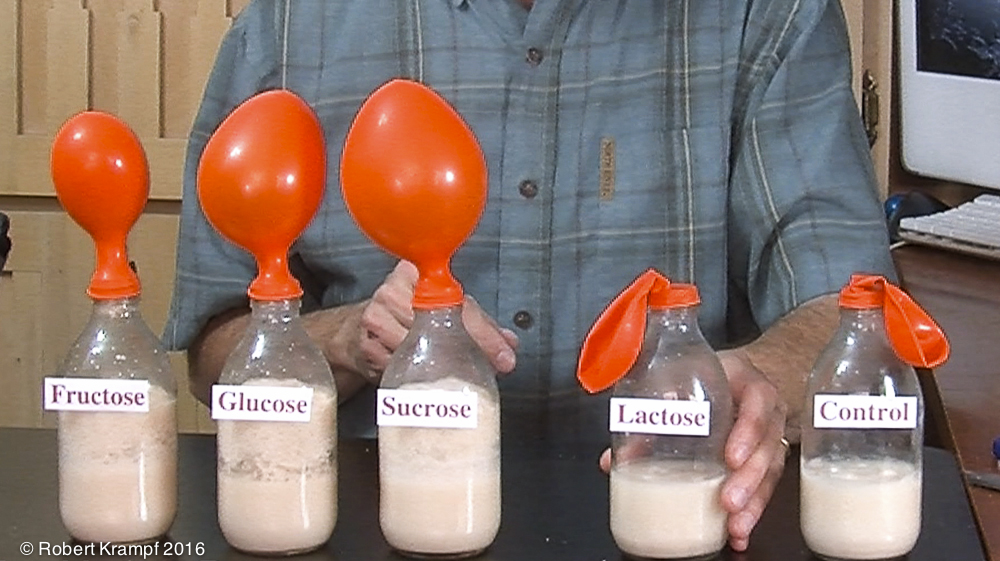

In the Yeast and Sugar video, I added different kinds of sugar to bottles with yeast and warm water. One of the bottles was a control. What should have been in that bottle?
-
Just water
No. With just water, you are removing two variables, the yeast and the sugar. You only want to remove the independent variable.
-
Water and yeast
Yes! A control should be exactly like the others, but without the independent variable (the variable you are changing in the experiment.) In this case, the variable you are changing is the kind of sugar, so the control should have everything except for the sugar. -
Water and sugar
No. The yeast is not the independent variable, so leaving it out would not be correct. -
Water and salt
No. Adding salt would be adding a new variable, which is not correct.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.N.1.4 Identify a control group and explain its importance in an experiment.
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Testing a Leaf for Starch | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
SC.7.N.1.4 Identify test variables (independent variables) and outcome variables (dependent variables) in an experiment.
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
3-5-ETS1-3 Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time.
