Here are some science questions from the Sixth, Seventh, and Eighth Grade Standards to help you test your knowledge of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time you reload the page.
* Click here to see only the most recently added questions.
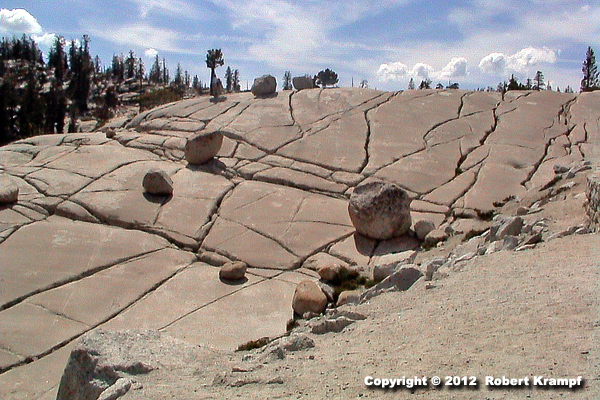

The large cracks in this rock are called expansion cracks. As the overlying rock erodes away, the rock expands, causing the cracks. The cracks are an example of:
-
Erosion
No. Erosion means that the pieces of rocks are being carried away. The overlying rocks have been eroded, but the cracks are not carrying the pieces to a new location. -
Weathering
Yes! As the rocks expand unevenly, tension builds up. When there is enough stress, the rocks break. That breaking of large rocks into smaller pieces is called weathering. -
Both erosion and weathering
No. The rocks are being broken (weathering), but the pieces are staying in place, so there is not erosion. -
Neither erosion nor weathering
No. The cracks show that the rocks are breaking, which is weathering..
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
SC.7.E.6.2 Identify the patterns within the rock cycle and relate them to surface events (weathering and erosion) and sub-surface events (plate tectonics and mountain building).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.2.b Distinguish between weathering (i.e., wearing down and breaking of rock surfaces) and erosion (i.e., the movement of materials).
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
UT.5.II.1.a Identify the objects, processes, or forces that weather and erode Earth’s surface (e.g., ice, plants, animals, abrasion, gravity, water, wind)
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
UT.8.III.2.b Describe the role of energy in the processes that change rock materials over time.
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
NGSS
4-ESS2-1 Make observations and/or measurements to provide evidence of the effects of weathering or the rate of erosion by water, ice, wind, or vegetation.
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |

This is Halite, also known as table salt. It was formed when ancient seas dried up, leaving layers of salt behind. What kind of rock is it?.
-
Igneous
No. Igneous rocks formed from magma or lava. The Halite was not melted, and is not an igneous rock. -
Sedimentary
Yes! Sedimentary rocks are deposited by wind, water, ice, or gravity, and they often contain fossils. Halite was deposited in large layers by water, which means that it is a sedimentary rock. Halite is also a mineral, and is one of the few rocks/minerals that we eat. -
Metamorphic
No. Metamorphic rocks have been changed by heat and pressure from a different kind of rock. It is not metamorphic. -
Halite is not a rock.
No. Halite is a naturally occurring solid that forms large layers in the Earth. Halite is a rock.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
SC.7.E.6.2 Identify the patterns within the rock cycle and relate them to surface events (weathering and erosion) and sub-surface events (plate tectonics and mountain building).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.a Describe the differences between minerals and rocks.
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
NGSS
4-ESS1-1 Identify evidence from patterns in rock formations and fossils in rock layers to support an explanation for changes in a landscape over time.
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Superposition | video |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Crosscutting | video |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Reading the Rocks: The Present is the Key to the Past | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Paleo Cookies | video |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
MS-ESS2-1 Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth’s materials and the flow of energy that drives this process.
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
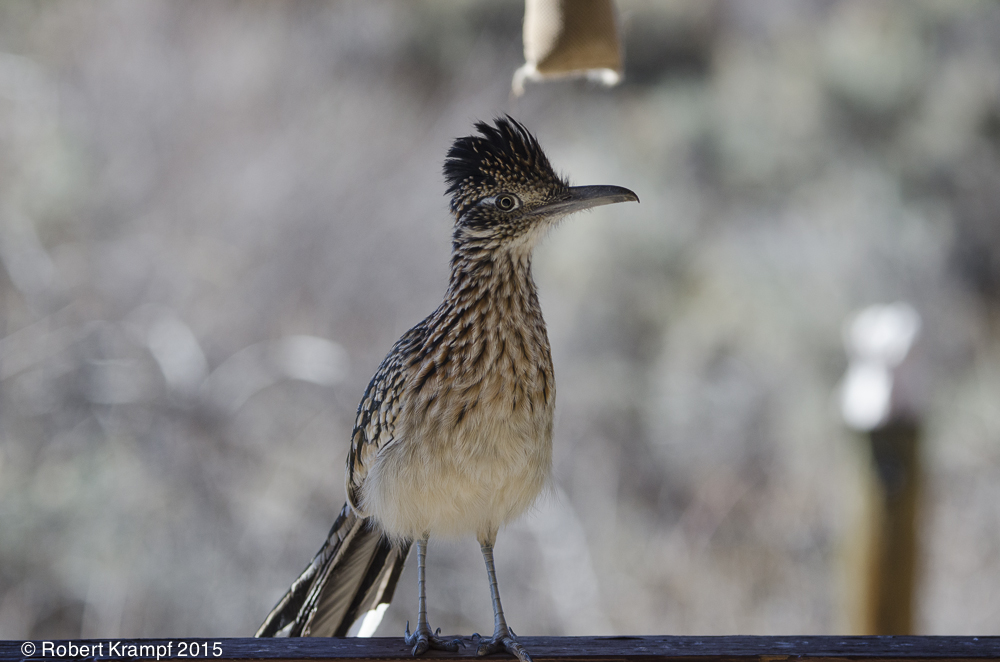

Which part of the food web does this roadrunner belong to?
-
Producer.
No. A producer captures energy from sunlight, and stores it as food. To do that, the organism needs to contain chlorophyll. -
Primary Consumer.
No. Primary consumers eat producers. In spite of what you may have seen in cartoons, roadrunners do not eat plants or bird seed. -
Secondary Consumer
Yes! Secondary consumers eat other consumers. Roadrunners are predators, and eat lizards, snakes, mice, and many other small animals. -
Decomposer
No. Roadrunners may occasionally scavenge freshly killed animals, but they are not decomposers.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.L.17.3 Trace the flow of energy from the Sun as it is transferred along the food chain through the producers to the consumers.
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
SC.7.L.17.1 Explain and illustrate the roles of and relationships among producers, consumers, and decomposers in the process of energy transfer in a food web.
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS3-1 Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun.
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
5-LS2-1 Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment.
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
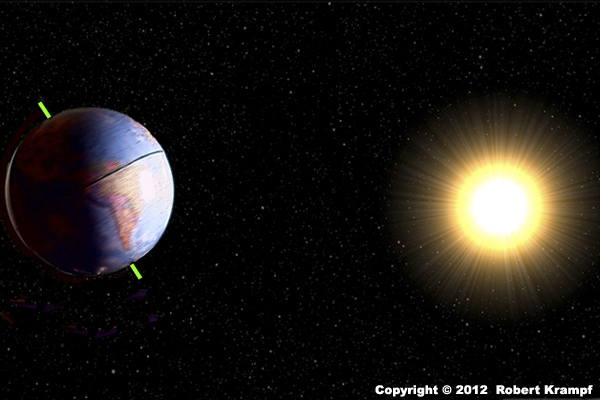
The Earth stays in orbit around the Sun because:
-
The Sun's gravity pulls on the Earth
This is only part of the answer. -
The Earth's gravity pulls on the Sun
This is only part of the answer. -
The gravity of the Sun and the Earth pull on each other
Yes! The gravitational attraction between the Earth and the Sun is a result of both the Sun pulling on the Earth and the Earth pulling on the Sun. -
Gravity does not keep the Earth in its orbit.
No. Without the pull of gravity, the Earth would continue moving in a straight path instead of curving around the Sun.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.P.13.1 Identify familiar forces that cause objects to move, such as pushes or pulls, including gravity acting on falling objects.
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Obedient Coin | video, checked |
| The Slow Race | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Magic Coin | video |
| Making a Compass | video, checked |
| Torque | video |
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Balancing a Meter Stick | text page |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
SC.8.E.5.9 Explain the impact of objects in space on each other including: 1. the Sun on the Earth including seasons and gravitational attraction 2. the Moon on the Earth, including phases, tides, and eclipses, and the relative position of each body.
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Why is a Full Moon So Bright? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
| Review Space-12 | practice |
SC.6.P.13.2 Explore the Law of Gravity by recognizing that every object exerts gravitational force on every other object and that the force depends on how much mass the objects have and how far apart they are.
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Force, Pressure, and Shoes | video, checked |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
Utah
UT.3.IV.2.c Pose questions about gravity and forces.
| Water in a Glass, part 2 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 3 | video, checked |
| Water in a Glass, part 1 | video, checked |
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Force, Pressure, and Shoes | video, checked |
| Balancing a Meter Stick | text page |
| Review Energy-8 | quest |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
UT.6.III.3.a Describe the forces holding Earth in orbit around the sun, and the moon in orbit around Earth.
| Review Space-13 | quest |
NGSS
MS-ESS1-2 Develop and use a model to describe the role of gravity in the motions within galaxies and the solar system.
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Space-13 | quest |
| Review Space-10 | practice |
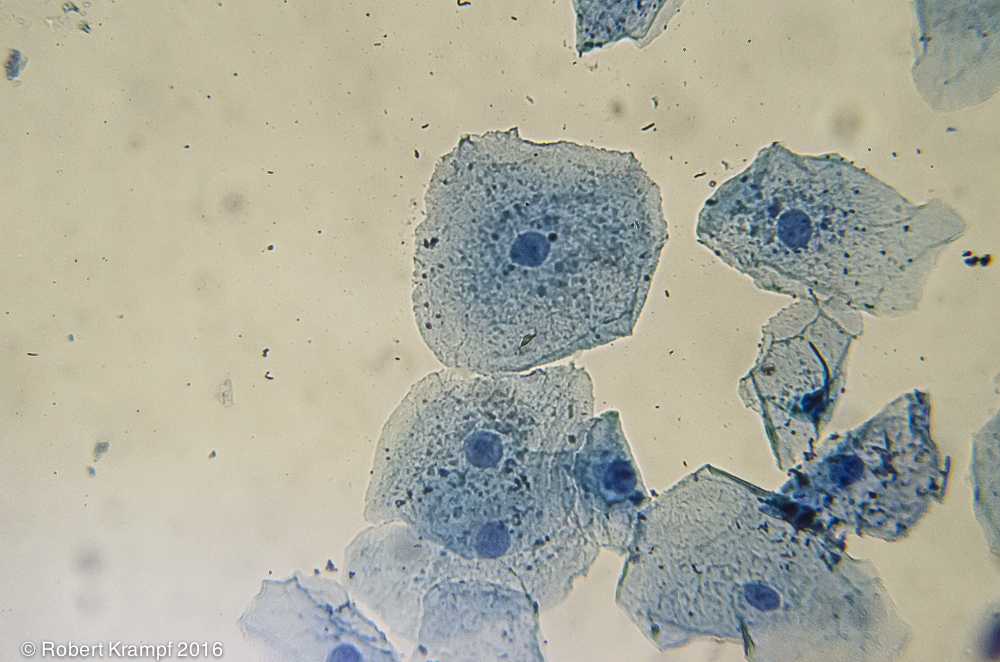
These cells DO NOT have a cell wall. What does that tell us?
-
These are young cells.
No. Even new cells can have a cell wall. -
These are NOT plant cells.
Yes! Plant cells are surrounded by a cell wall, which provides structure and protection. -
These are NOT animal cells.
No. Animal cells do not have a cell wall. -
These are dead cells.
No. Being alive or dead does not change whether a cell has a cell wall or not.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.6.L.14.4 Compare and contrast the structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles.
| Osmosis | video, checked |
| Review Cells-1 | practice |
| Review Cells-2 | practice |
| Review Cells-3 | practice |
| Review Cells-4 | practice |
Utah
UT.7.III.1.c Differentiate between plant and animal cells based on cell wall and cell membrane.
| Review Cells-1 | practice |
| Review Cells-2 | practice |
NGSS
MS-LS1-2 Develop and use a model to describe the function of a cell as a whole and ways parts of cells contribute to the function.
| Osmosis | video, checked |
| Review Cells-1 | practice |
| Review Cells-2 | practice |
| Review Cells-3 | practice |
| Review Cells-4 | practice |
