Here are some science questions from the Sixth, Seventh, and Eighth Grade Standards to help you test your knowledge of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time you reload the page.
* Click here to see only the most recently added questions.

This is a photograph of the Painted Desert in Arizona. These layers of rock have not been folded or overturned, so we know that the layer on the bottom is the oldest. This is based on:
-
The Law of Superposition
Yes! The Law of Superposition tells us that unless the layers have been disturbed, they will be in order of their age, with the youngest on the top, and the oldest on the bottom. -
The Law of Crosscutting
No. The Law of Crosscutting tells us that a feature (crack, fault, igneous intrusion, etc.) that cuts through a layer of rock is younger than the layer it cuts through. That makes sense, because the layer would have to be there first, before it could be broken by a fault, etc. -
The Law of Relativity
No. There is a theory of relativity, which deals with the basics of physics, not geology. There is no Law of Relativity. -
The Law of Thermodynamics
No. The Law of Thermodynamics deals with energy, not with layers of rock.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.7.E.6.3 Identify current methods for measuring the age of Earth and its parts, including the law of superposition and radioactive dating.
| Imagining Geologic Time | video |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Superposition | video |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Crosscutting | video |
| Reading the Rocks | text page |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.III.3.c Explain why some sedimentary rock layers may not always appear with youngest rock on top and older rocks below (i.e., folding, faulting).
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
NGSS
4-ESS1-1 Identify evidence from patterns in rock formations and fossils in rock layers to support an explanation for changes in a landscape over time.
| Paleo Cookies | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Superposition | video |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Crosscutting | video |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Reading the Rocks: The Present is the Key to the Past | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
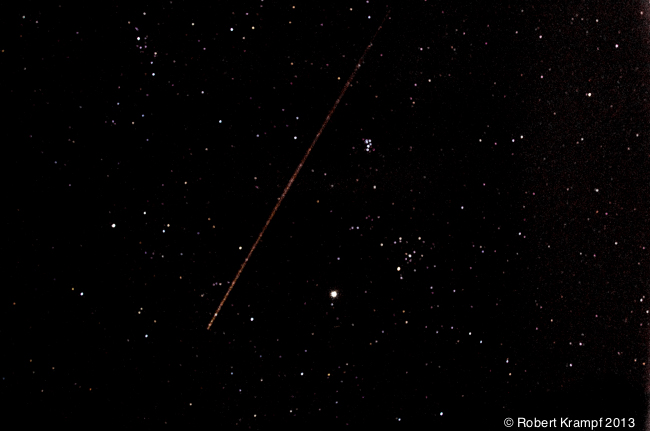

Which of the following is a difference between a meteor and a comet?
-
Meteors are mostly made up of ice.
No. Meteors are made up of rock or iron, Comets are mostly made up of ice. -
Only comets have a visible tail.
No. A meteor is a meteoroid that has entered our atmosphere. As it burns, it also produces a tail. -
Meteors seem to move faster because they are closer.
Yes. Meteors are entering our atmosphere, so they are much closer to us that a distant comet. That makes them seem to move much faster. -
Comets are smaller than meteors.
No. Meteors are small, often the size of a grain of sand. Comets are much larger.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.E.5.3 Distinguish among the following objects of the Solar System – Sun, planets, moons, asteroids, comets – and identify Earth’s position in it.
>>> Teacher Page: Our Solar System
| Making a Scale Model of the Solar System | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| How Far is That Planet? | text page |
| Review Space-3 | practice |
SC.8.E.5.3 Distinguish the hierarchical relationships between planets and other astronomical bodies relative to solar system, galaxy, and universe, including distance, size, and composition.
| Making a Scale Model of the Solar System | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| How Far is That Planet? | text page |
| Review Space-3 | practice |
| Review Space-2 | practice |
| Review Space-10 | practice |
Utah
UT.6.III.1.d Describe the characteristics of comets, asteroids, and meteors.
| Review Space-3 | practice |
NGSS
MS-ESS1-3 Analyze and interpret data to determine scale properties of objects in the solar system.
| Making a Scale Model of the Solar System | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| How Far is That Planet? | text page |
| Review Space-3 | practice |
| Review Space-2 | practice |
| Review Space-4 | practice |
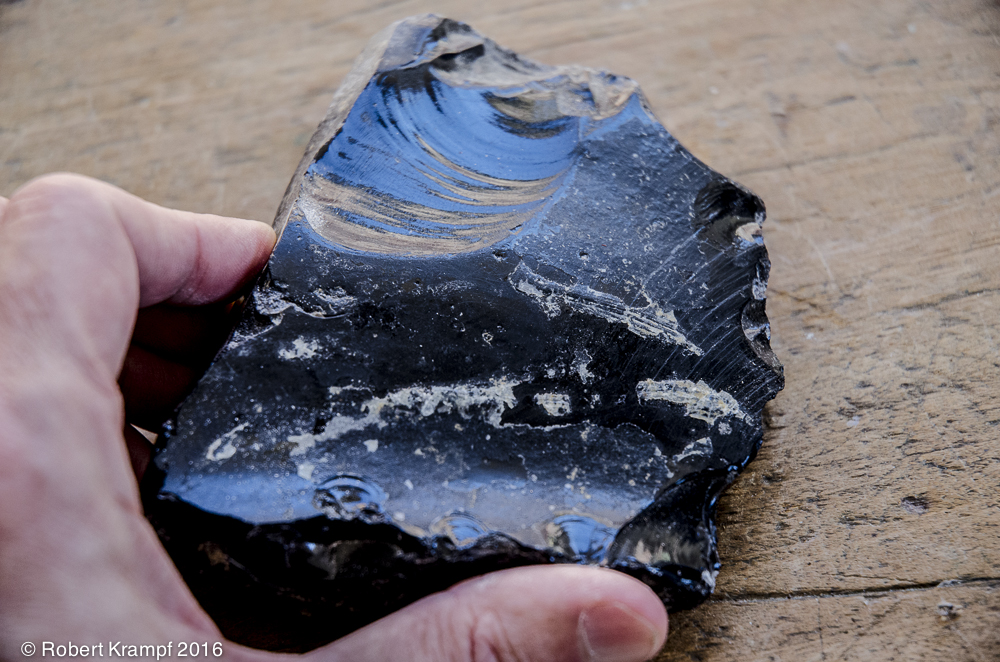

This is called Obsidian. It is formed from molten lava that cools so quickly that it forms a natural glass instead of crystals. What kind of rock is it?.
-
Igneous
Yes! Igneous rocks formed from magma or lava. This is an igneous rock. -
Sedimentary
No. Sedimentary rocks are deposited by wind, water, ice, or gravity, and they often contain fossils. This is not a sedimentary rock. -
Metamorphic
No. Metamorphic rocks have been changed by heat and pressure from a different kind of rock. Instead of being changed, this got hot enough to completely melt, so it is not metamorphic. -
Obsidian is not a rock.
No. Obsidian is a naturally occurring solid that forms large layers in the Earth. Obsidian is a rock.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
SC.7.E.6.2 Identify the patterns within the rock cycle and relate them to surface events (weathering and erosion) and sub-surface events (plate tectonics and mountain building).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.a Describe the differences between minerals and rocks.
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
NGSS
4-ESS1-1 Identify evidence from patterns in rock formations and fossils in rock layers to support an explanation for changes in a landscape over time.
| Paleo Cookies | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Superposition | video |
| Reading the Rocks: Law of Crosscutting | video |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Reading the Rocks: The Present is the Key to the Past | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Geologic Time-1 | practice |
MS-ESS2-1 Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth’s materials and the flow of energy that drives this process.
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
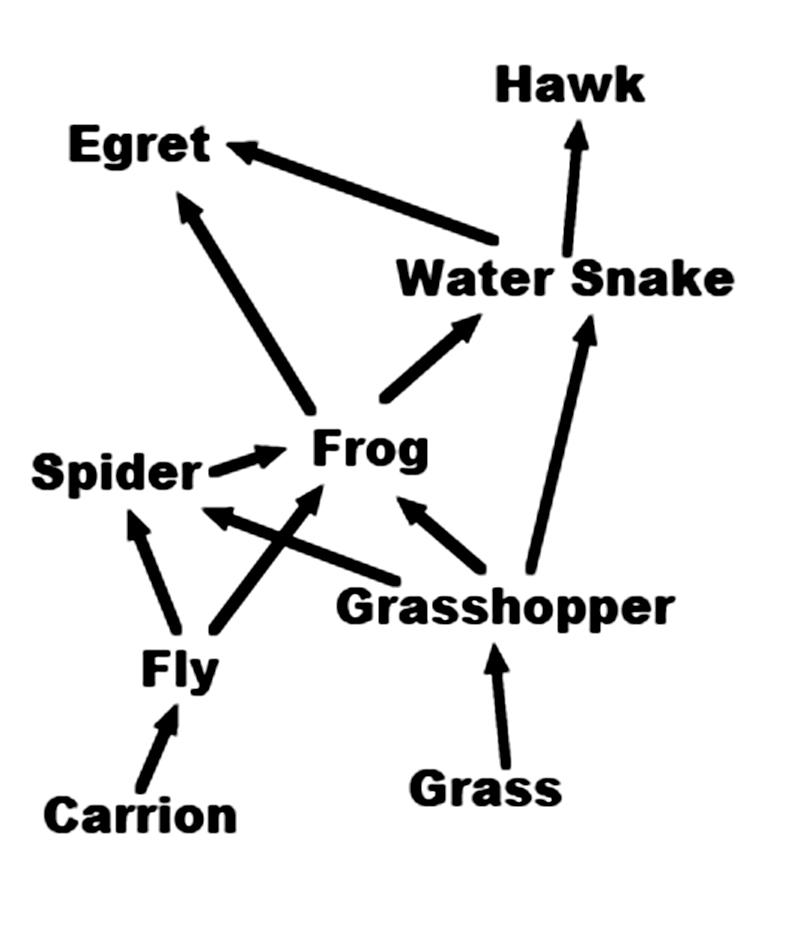
This is a simple chart showing how energy flows through some of the parts of a food web. For example, the arrow from the grass to the grasshopper shows that the grasshopper gets it energy by eating the grass.
The hawk gets its energy by eating the water snake, but there is no arrow leading from the hawk. What should the arrow from the hawk point to>
-
Egret
No. The egret does not eat hawks. -
Carrion
Yes! Carrion is dead animals. When the hawk eventually dies, flies will get their energy by eating the dead body. You could also draw arrows from all of the other animals to carrion. -
The Sun
No. The Sun is not on the chart, and The Sun does not get its energy from the hawk. -
There should not be an arrow leading from the hawk.
No. Energy cannot be destroyed. It always goes back into the system.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.L.17.3 Trace the flow of energy from the Sun as it is transferred along the food chain through the producers to the consumers.
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Food Web Tag | text page |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
SC.8.L.18.4 Cite evidence that living systems follow the Laws of Conservation of Mass and Energy.
| Thoughts on Trees | text page |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
Utah
UT.8.II.2.a Categorize the relationships between organisms (i.e., producer/consumer/decomposer, predator/prey, mutualism/parasitism) and provide examples of each.
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-11 | practice |
| Review Food Web-12 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
NGSS
5-PS3-1 Use models to describe that energy in animals’ food (used for body repair, growth, motion, and to maintain body warmth) was once energy from the sun.
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Calories | video, ClosedCaptions, checked |
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Measuring Photosynthesis | video, checked |
| Calories: Measuring the Energy | text page, free |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
5-LS2-1 Develop a model to describe the movement of matter among plants, animals, decomposers, and the environment.
| Scavengers and Decomposers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated |
| Secondary Consumers | video, free, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| Producers | video, free, Updated, checked |
| Primary Consumers | video, ClosedCaptions, Updated, checked |
| What is a Food Web? | text page, free, checked |
| Review Food Web-1 | practice |
| Review Food Web-3 | practice |
| Review Food Web-4 | practice |
| Review Food Web-5 | practice |
| Review Food Web-6 | practice |
| Review Food Web-7 | practice |
| Review Food Web-8 | practice |
| Review Food Web-9 | practice |
| Review Food Web-10 | practice |
| Review Food Web-2 | practice |
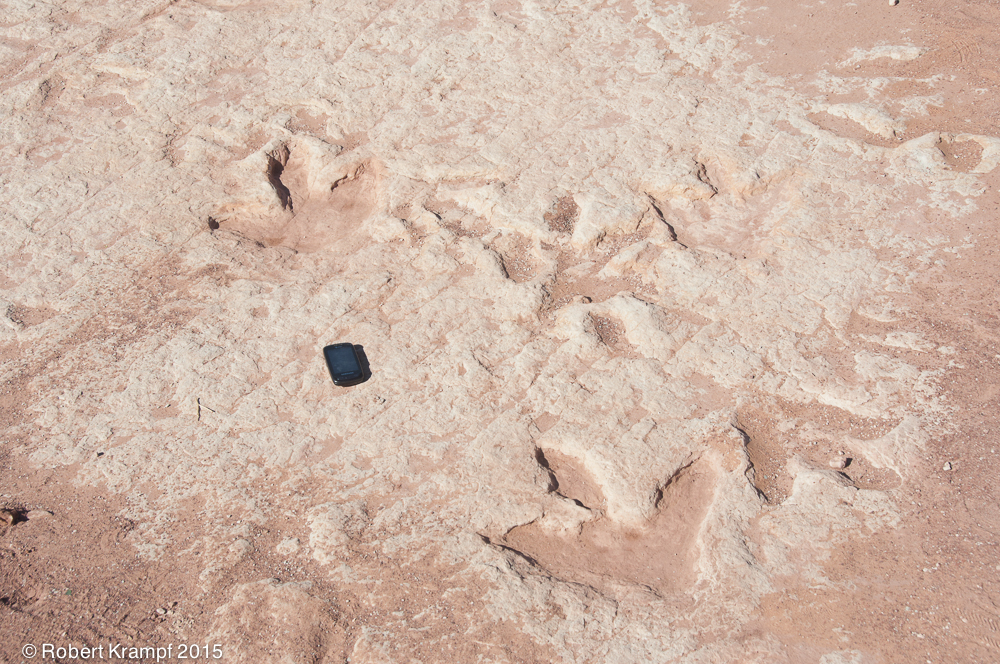

This layer of rock contains fossilized tracks from a dinosaur (Dilophosaurus). The black object is my cell phone for size reference. What kind of rock is it?
-
Igneous
No. Igneous rocks formed from magma or lava. An igneous rock would not have fossilized dinosaur tracks. -
Sedimentary
Yes! Sedimentary rocks are deposited by wind, water, ice, or gravity, and they often contain fossils. The presence of fossils is one of the indications that a rock is probably sedimentary. -
Metamorphic
No. Metamorphic rocks have been changed by heat and pressure from a different kind of rock. The metamorphic process would have destroyed the tracks. -
It is not rock.
No. These dinosaur tracks are in rock.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.1.d Classify common rocks found in Utah as sedimentary (i.e., sandstone, conglomerate, shale), igneous (i.e., basalt, granite, obsidian, pumice) and metamorphic (i.e., marble, gneiss, schist).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
UT.8.III.1.c Categorize rock samples as sedimentary, metamorphic, or igneous.
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
NGSS
MS-ESS2-1 Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth’s materials and the flow of energy that drives this process.
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Definition of a Mineral | video, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| What is a Mineral? | video, checked |
| Identifying Minerals | video, learnalong |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
