Here are some science questions from the Standards for Grades 2-5 to help you test your knowledge of the Next Generation Sunshine State Standards.
The questions are chosen randomly, so this quest will be different each time you reload the page.
* Click here to see only the most recently added questions.

Are the ocean waves crashing against this rock an example of:
-
Erosion
Partially right! This is an example of erosion. Sand and bits of the rock are being moved by the waves.. -
Weathering
Partially right! This is an example of weathering too. Weathering is when a rock is broken into smaller pieces. The waves and the sand they carry are slowly grinding away these rocks. -
Both erosion and weathering
Yes! The rock is being broken into smaller pieces by the waves (weathering), and the pieces are also being carried away by the waves (erosion). -
Neither erosion nor weathering
No. Both weathering and erosion are happening here.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.6.1 Identify the three categories of rocks: igneous, (formed from molten rock); sedimentary (pieces of other rocks and fossilized organisms); and metamorphic (formed from heat and pressure).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Homemade Fossil Dig | text page |
| Foliated and Unfoliated Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Identifying Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous Rocks | text page, learnalong |
| Light and Dark Minerals | text page, learnalong |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Rocks-2 | practice |
| Review Rocks-3 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
SC.7.E.6.2 Identify the patterns within the rock cycle and relate them to surface events (weathering and erosion) and sub-surface events (plate tectonics and mountain building).
| Evaporites | video, learnalong, checked |
| What is a Rock? | video, learnalong, checked |
| The Rock Cycle | video, learnalong |
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Bioclastics: Rocks With No Minerals | video |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Rocks-9 | practice |
| Review Rocks-7 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-10 | practice |
| Review Rocks-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-4 | practice |
| Review Rocks-5 | practice |
| Review Rocks-6 | practice |
| Review Rocks-8 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.III.2.b Distinguish between weathering (i.e., wearing down and breaking of rock surfaces) and erosion (i.e., the movement of materials).
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
UT.5.II.1.a Identify the objects, processes, or forces that weather and erode Earth’s surface (e.g., ice, plants, animals, abrasion, gravity, water, wind)
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
UT.8.III.2.b Describe the role of energy in the processes that change rock materials over time.
| Igneous Rocks and Bubbles | video, free, learnalong, Updated |
| Sedimentary Rocks | video, learnalong |
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
NGSS
4-ESS2-1 Make observations and/or measurements to provide evidence of the effects of weathering or the rate of erosion by water, ice, wind, or vegetation.
| Change: Fast and Slow | video |
| Erosion | video, checked |
| Continuous Change | video, checked |
| Weathering and Erosion | video, learnalong, checked |
| Review Erosion-1 | practice |
| Review Erosion-2 | practice |
| Review Erosion-3 | practice |
| Review Erosion-4 | practice |
| Review Erosion-5 | practice |
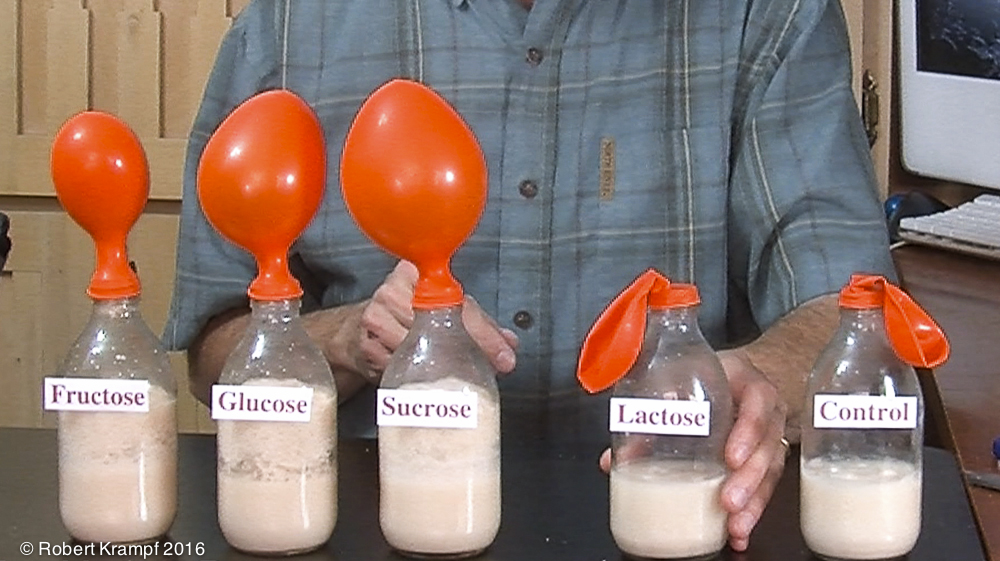

In the Yeast and Sugar video, I added different kinds of sugar to bottles with yeast and warm water. One of the bottles was a control. What should have been in that bottle?
-
Just water
No. With just water, you are removing two variables, the yeast and the sugar. You only want to remove the independent variable.
-
Water and yeast
Yes! A control should be exactly like the others, but without the independent variable (the variable you are changing in the experiment.) In this case, the variable you are changing is the kind of sugar, so the control should have everything except for the sugar. -
Water and sugar
No. The yeast is not the independent variable, so leaving it out would not be correct. -
Water and salt
No. Adding salt would be adding a new variable, which is not correct.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.N.1.4 Identify a control group and explain its importance in an experiment.
| Bacteria and Antibiotics | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Testing a Leaf for Starch | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
SC.7.N.1.4 Identify test variables (independent variables) and outcome variables (dependent variables) in an experiment.
| Floating Cups | video, checked |
| Testing for Tannic Acid | video |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |
Utah
NGSS
3-5-ETS1-3 Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-1 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-2 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-9 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-11 | practice |

How hot does an area have to be to be classified as a desert?
Answer:
Deserts are defined by lack of precipitation, not by temperature. They are areas where precipitation minus evaporation yields less than 10 inches of rain per year. The largest desert on Earth is in Antarctica, a very cold place.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.5.E.7.6 Describe characteristics (temperature and precipitation) of different climate zones as they relate to latitude, elevation, and proximity to bodies of water.
| Weather and Climate | video |
| Review Weather-7 | practice |
| Review Weather-9 | practice |
Utah
UT.4.V.1.c Locate examples of areas that have characteristics of wetlands, forests, or deserts in Utah.
| Review Weather-7 | practice |
| Review Weather-9 | practice |
NGSS
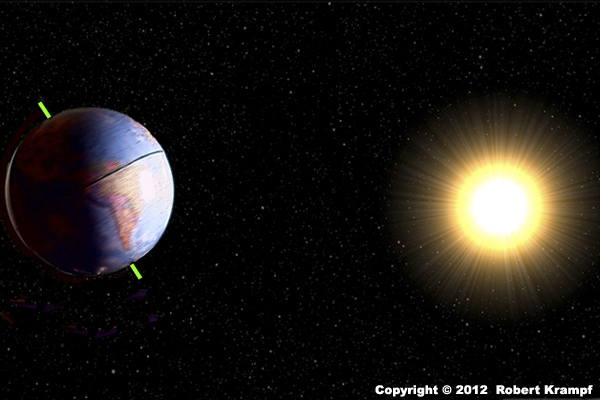
It takes the Earth 24 hours to:
-
Rotate
Yes. The Earth turns on its axis to make one full rotation every 24 hours. -
Revolve
No. It takes a year for the Earth to revolve around the Sun. -
Orbit
No. It takes a year for the Earth to orbit around the Sun. -
Reverse
No. The motion of the Earth does not reverse.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.4.E.5.3 Recognize that Earth revolves around the Sun in a year and rotates on its axis in a 24-hour day.
| Making a Scale Model of the Solar System | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Finding Your Way | video, checked |
| Review Space-11 | practice |
SC.8.E.5.7 Compare and contrast the properties of objects in the Solar System including the Sun, planets, and moons to those of Earth, such as gravitational force, distance from the Sun, speed, movement, temperature, and atmospheric conditions.
| Making a Scale Model of the Solar System | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Planets and Pennies | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Space-4 | practice |
| Review Space-11 | practice |
Utah
UT.3.I.2.a Describe the motions of Earth (i.e., the rotation [spinning] of Earth on its axis, the revolution [orbit] of Earth around the sun).
| Global Science | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Space-11 | practice |
UT.6.I.2.a Identify the difference between the motion of an object rotating on its axis and an object revolving in orbit.
| Review Space-11 | practice |
NGSS

What do you have to do to replicate an experiment?
-
You do the same experiment several times.
No. Doing the same experiment several times is repetition, not replication. -
You do the same experiment that someone else did.
Yes. By replicating an experiment exactly, you should get the same results as the original experiment. -
You do an improved version of someone's experiment.
For replication, you do the experiment exactly as the original scientist did, without making any changes. -
You look for errors in someone's experiment.
The purpose of replication is to verify, not to look for errors.
Click to see which state standards this question tests, and which of my videos, experiments, and other resources support that topic.
Florida
SC.2.N.1.4 Explain how particular scientific investigations should yield similar conclusions when repeated.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
SC.5.N.2.2 Recognize and explain that when scientific investigations are carried out, the evidence produced by those investigations should be replicable by others.
>>> Teacher Page: Nature of Science and Dissolving
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
SC.6.N.1.2 Explain why scientific investigations should be replicable.
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
SC.7.N.1.2 Differentiate replication (by others) from repetition (multiple trials).
| What is Science? | video, ClosedCaptions |
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
SC.8.N.1.2 Design and conduct a study using repeated trials and replication.
| What is Science?: Repeat and Replicate | video |
| Review Scientific Process-6 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-5 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-7 | practice |
| Review Scientific Process-10 | practice |
